Syllabus#
Logistics#
Course name: Comp-526
Course term: Fall 2025
Class time: M-W-F: 11:00 am - 11:50AM am
Mode of delivery: in person
Location: LH 347
Instructor: Valeria Barra#
Pronouns: (she/her/hers)
Email: vbarra [at] sdsu [dot] edu
Office location: announced on the course Canvas page
Office Hours: announced on the course Canvas page or by appointment.
Tip
Office hours are an important time for asking questions, solving problems, discussing broader academic and career strategies, and providing feedback so I can make the class serve your needs and those of people with similar experiences and interests.
Overview#
Scientific computing and mathematical modeling (both deterministic and stochastic) are fundamental tools for the solution of problems arising in the study of complex systems, whether originating from the physical, chemical, or biological sciences, or of an economic and social nature.
Scientific computing is a broad term that describes the use of computers for scientific, medical, and engineering applications. This definition is often application-focused or domain-driven.
On the other hand, Numerical Analysis, is used to solve problems in analysis (i.e., with real numbers) by numerical, rather than symbolic means. Some examples:
Solving linear and nonlinear equations
Computing values of definite integrals
Solving differential equations
This can be seen as a problem-focused description.
Numerical (or Computational) Methods are algorithms (methods) for solving mathematical problems in the service of applications. Some examples:
The method of conjugate gradients for linear systems
Gaussian quadrature for computing integrals
The Runge-Kutta method for initial value problems
This is an algorithm-focused description. In reality, this area encompasses all three: based on an application, we formulate some mathematical problems and find an algorithm for it to solve it using computers.
Organization and course design#
We will start by giving an introduction to version control and reproducibility, which are key aspects of modern computational sciences. The foundations learned during the first lecture will serve as the basis for the workflow that you will utilize throughout the semester for assignments and project submissions (it might be useful to review carefully the first lecture multiple times). Then we will introduce the Linux filesystem and some basic shell commands.
We’ll proceed with the evaluation of functions and introduce the concepts of conditioning and stability, which are applicable to every topic we encounter.
Then we’ll explore rootfinding, our first infinite algorithm, in which we’ll learn about convergence classes and the fundamental challenge of writing a function that is correct for all well-typed inputs.
We’ll move to the concepts of stability and backward stability.
Next up will be an introduction to linear algebra, interpolation, and then differentiation.
We’ll move on to integration and finally numerical solution of differential equations.
Although we’ll continue with new content, during the semester we will have two separate short modules on compiled languages programming: C and Fortran.
Towards the end of the semester, for your final projects, you can then form small teams of like interest and work on an original study (numerical experiments and interpretation, comparisons, etc.) or on contribution to be shared with the community. Studies and contributions can take many forms.
Student Learning Outcomes#
Upon completing this course, students will be able to
contribute to collaborative software with the use of version control systems, such as
gitformulate problems in science and engineering in terms of computational methods
evaluate the accuracy and performance of algorithms
diagnose ill-conditioned problem formulations and unstable algorithms
develop effective numerical software, taking into account stability, accuracy, and cost
communicate about the above using figures, numerical experiments, writing, and presentation
search for and understand relevant literature and documentation
write programs in Julia, C, and Fortran
Expectations#
Enter with a growth mindset, practice adaptive coping, and nurture your intrinsic motivation
Attend class (in-person) and participate in discussions
Make an honest attempt at activities, projects, etc.
Interact with the class notebooks and read reference material
Individual or group projects

Assessment, grading policy and schedule#
This class will have some assignments and projects (midterm and final). The final projects can be individual or group projects (depending on the number of students registered) and will be agreed upon with the instructor. There will be a midterm and a final oral presentation for each project. Moreover, a final report must be delivered. Instructions about what is expected for both midterm and final presentations as well as for the final report will be provided.
Grading breakdown:
Participation (can include engagement in class, attendance, use of office hours, etc) (5% - includes a graded quiz (1%) with due date Wednesday 09/10/25, by midnight (AOE))
Assignment 1 (10%): due date Friday 09/12/25, by midnight (AOE)
Assignment 2 (10%): due date Friday 09/26/25, by midnight (AOE)
Assignment 3 (10%): due date Friday 10/10/25, by midnight (AOE)
Assignment 4 (10%): due date Monday 11/10/25, by midnight (AOE)
AOE: Anywhere on Earth time zone. This time zone is 12 hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and typically used for online submissions to accommodate people from different time zones. Given that this course is taught in person in the Pacific standard time, I use this not really to facilitate submissions from different time zones, but to allow people not to worry about submitting by midnight sharp. This does not mean that I encourage people working late. I actually advocate for a healthy work/life balance for everyone (students and instructors alike).
Midterm Project (20%): The midterm/final project choice and proposal will need to be discussed with your teacher, before its submission (not via email). Please make sure to use plenty of Office Hours to discuss your midterm/final project Proposal before submitting it. This project is broken down in two deadlines. Please note that Canvas does not allow setting multiple parts with different deadlines for a given assignment. For the Midterm Project, I will set the earliest of the two deadlines on Canvas.
Part 1, due Friday 10/17/25, by midnight (AOE): Community project analysis and proposal.
Part 2, due Friday 10/31/25, by midnight (AOE): Community project contribution proposal and creation of an Issue.
Final Project (35%): This project is broken down in three deadlines. Please note that Canvas does not allow setting multiple parts with different deadlines for a given assignment. For the Final Project, I will set the latest of the three deadlines on Canvas.
Part 1, due Wednesday 11/19/25 by midnight (AOE): Creation of a Pull/Merge Request
Part 2, Friday 12/05/25, Monday 12/08/25 and Wednesday 12/10/25: In class oral presentations.
Part 3, due Wednesday 12/10/25, by midnight (AOE): submission of Final Project Report.
Assignments will be distributed no later than a week prior to the due date.
The schedule is subject to change (the instructor will announce any changes).
Late submission and absences policy: If you submit your assignments late, there is an increasing penalty (10% off for up to 24 hours late, 20% off for 24-48 hours late). No assignments will be graded if submitted later than 48 hours late.
Grading scale: The following grading scale will be used
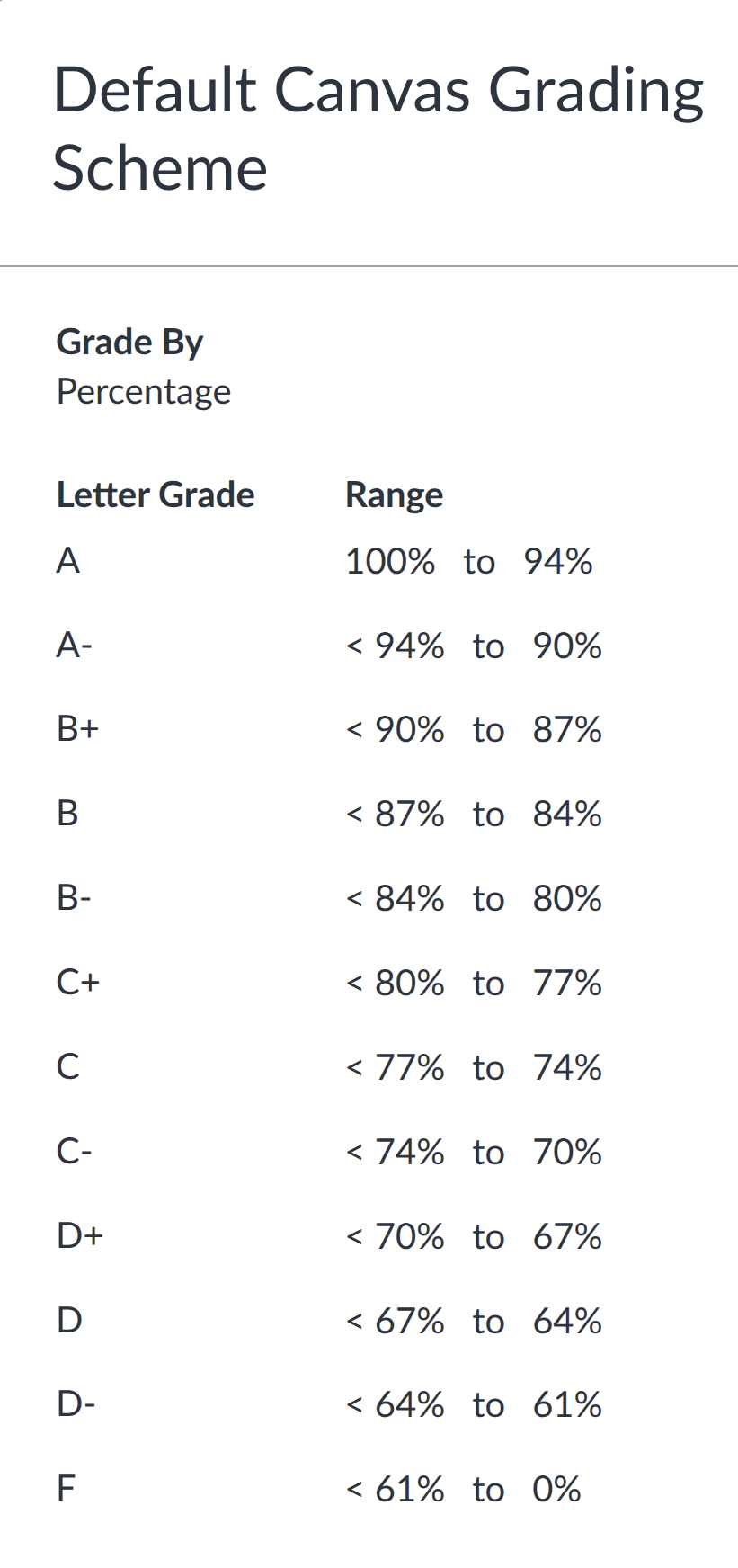
Grade questions/disputes: All questions regarding grading must be received no later than 5 days from the date grades are posted in Canvas.
Any student who cannot attend class or submit assignments by their due date for serious issues (e.g., medical emergencies) or participation in university activities (e.g., official university travel for conferences or sports) that can be documented, should communicate those to your instructor as soon as possible before the deadline.
Details on Midterm and Final projects#
Why community projects?#
Nowadays, the vital role of scientific software in research is widely recognized. Moreover, modern science is often conducted by large, collaborative multi-institutional aggregate teams scattered across the globe. To facilitate work across teams and to promote partnerships and collaborations, it is crucial for students to be exposed to open-source community projects and learn the best practices and standards by making contributions via software. If you are still unsure, check this reference “Why contribute to open source?” from the How to Contribute to Open Source guide.
Community contributions and analysis#
Over the course of the semester, you will follow the development activities of an active open source project of your choosing. This should be a project with an active developer community, hopefully from multiple institutions, that discuss their rationale in public, such as a mailing list and/or GitHub/GitLab Issues and Pull Requests or Slack/Discord channels. You will write and present about the performance and capability needs of key stakeholders, the way project resources are allocated, their metrics for success, and any notable achievements made over the course of the semester.
Your Final Project will be to make a contribution to be merged by the project of your choice. Adding new examples and/or improving documentation are extremely valuable contributions, but you may also add features or improve implementations. You can also analyze an existing bug or working example, comment on the implementation performance, and compare with other similar implementations from other packages/libraries. Please respect the time of project maintainers and reviewers by learning about the project and its expectations and process, communicating in advance, and leaving plenty of time for multiple rounds of review and revision.
GitHub#
We’ll use Git with GitHub Classroom for managing activities and feedback.
Tip
If you don’t have a GitHub account, follow these instructions from the SDSU Research & Cyberinfrastructure website and link it to your SDSUid.
Use a personal email account rather than the SDSU one, so that you won’t have problems accessing your GitHub account in the future.
Choose your username wisely! Most likely you will use this again in professional settings in your career.
The last commit to the GitHub repository made before the deadlines will be the one used to determine your grade. Students can modify their submitted files as many times as they want before their due date without incurring in any late penalty fee. If students modify any submitted file after the posted deadline, they are subject to the late penalty fees outlined in the Late submission policy above.
Course materials, programming languages and environment#
I will provide all free course materials and suggested readings on the class website. If you prefer to read a print-out version, please talk to me. I will primarily use Julia and Jupyter notebooks for slides and activities in class. This environment is convenient to work with, general purpose, and has extensive library support. It is possible to write fast code in Julia, though performance implications can be mysterious. C, C++, and Fortran are popular languages for writing production numerical software, sometimes called from a higher level programming language like Python. MATLAB is also popular for numerical computing, though it is a proprietary environment and lacks general-purpose libraries.
Most HPC facilities use a Linux operating system and many open source software packages and libraries will have the best documentation and testing on Linux systems. You can use any environment for your local development environment, or use the SDSU’s JupyterHub to experiment and develop without a local install. If you have never logged in before, check SDSU’s Research & Cyberinfrastructure resources for students.
Target audience#
Students in computational science, applied mathematics, or a quantitative science or engineering field.
Catalog Prerequisites:
MATH 252: Calculus III
MATH 254: Introduction to Linear Algebra
Good to know:
Matrix theory
Integration
Partial differentiation
Classroom Behavior#
Both students and faculty are responsible for maintaining an appropriate learning environment in all instructional settings, whether in person, remote, or online. Those who fail to adhere to such behavioral standards may be subject to discipline. Professional courtesy and sensitivity are especially important with respect to individuals and topics dealing with race, color, national origin, sex, pregnancy, age, disability (visible or invisible), creed, religion, sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, veteran status, political affiliation, or political philosophy.
Resources for students#
Every student is encouraged to read the SDSU Student Academic Success Handbook (includes essential information for students). Please, watch this video from the Basic Needs Center and Economic Crisis Response Team (ECRT).
Accommodation for Disabilities#
If you think you may qualify for accommodations because of a disability, please contact SDSU Student Ability Success Center and make your faculty member aware in a timely manner so that your needs can be addressed. Please allow 10-14 business days for this process.
Preferred Student Names and Pronouns#
We recognize that students’ legal information doesn’t always align with how they identify. Class rosters are provided to the instructor with the student’s legal name. If you feel that the name that appears on the class roster does not reflect your preferred name or pronoun, let your faculty member know.
Academic Honesty#
SDSU has strict codes of conduct and policies regarding cheating and plagiarism. Become familiar with the policy and what constitutes plagiarism. Any cheating or plagiarism will result in failing this class and a disciplinary review by the University. These actions may lead to probation, suspension, or expulsion.
Use of AI#
This course requires you to complete various assignments that assess your understanding and application of the course content. You are expected to do your own work and cite any sources you use and collaborators (humans or not) appropriately. You are personally responsible for understanding and verifying the code that you submit and include appropriate documentation.
The California State University system requires instructors to report all instances of academic misconduct to the Center for Student Rights and Responsibilities. Academic dishonesty will result in disciplinary review by the University and may lead to probation, suspension, or expulsion. Instructors may also, at their discretion, penalize student grades on any assignment discovered to have been produced in an academically dishonest manner such as cheating and plagiarism as described on the Cheating and Plagiarism page.
In May 2024, the University Senate extended its definition of plagiarism to include the un-cited use of generative AI applications, specifically: “representing work produced by generative Artificial Intelligence as one’s own.” Academic freedom ensures that instructors are empowered to determine whether students may use genAI in their classes and to what extent. To minimize confusion, we report here a statement regarding the use of AI in this class.
Instructor Approved Use of LLMs: Students should not use generative AI applications, known as large language models (LLMs), in this course except as approved by the instructor. Any use of generative AI outside of instructor-approved guidelines constitutes misuse. Misuse of generative AI is a violation of the course policy on academic honesty and will be reported to the Center for Student Rights and Responsibilities. LLMs, such as OpenAI’s chatGPT, Microsoft’s Co-Pilot, Anthropic’s Claude, Meta’s Llama, Google’s Gemini, or VSCode AI assistant etc. are valuable tools, which are still in their infancy, that will likely transform how we teach, learn, and code. However, such LLMs are highly sensitive to the (often biased) data that they are trained on and prone to hallucinations leading to inaccurate and unreliable results. Hence, it is necessary for the user to have a firm grasp and understanding of the material.
Work created by AI tools may not be considered original work and instead, considered automated plagiarism. It is derived from previously created texts from other sources that the models were trained on, yet doesn’t cite sources.
AI models have built-in biases (ie, they are trained on limited underlying sources; they reproduce, rather than challenge, errors in the sources)
AI tools have limitations (ie, they lack critical thinking to evaluate and reflect on criteria; they lack abductive reasoning to make judgments with incomplete information at hand)
Given these important ethical caveats, it is crucial for students to learn how to use these tools and other online resources (e.g., stackoverflow.com) responsibly. For my class
You must acknowledge and cite use of examples and aids that you include in your assignments, whether from LLMs or other sources.
You must clearly identify the use of AI-based tools in your work. Any work that utilizes AI-based tools must be clearly marked as such, including the specific tool(s) used. For example, if you use ChatGPT-3, you must cite “ChatGPT-3. (YYYY, Month DD of query). “Text of your query and answers”.
You must not use AI-based tools to write commentaries/reports/essays, but use your own words for those.
You must be transparent in how you used the AI-based tool, including what work is your original contribution.
You must ensure your use of AI-based tools does not violate any copyright or intellectual property law.
You must not use AI-based tools to cheat on assessments.
You must not use AI-based tools to plagiarize without citation.
In order to prevent misuse of these tools and to ensure students are adequately learning the material, the Instructor may ask students in class or during office hours about certain topics covered in this course after they have been introduced and the students’ answers will contribute to the overall assessment and grades. Instructors and graders/TAs may also use AI detector tools. If you are found in violation of this policy, you may face penalties such as a reduction in grade, failure of the assignment or assessment, or even failure of the course. Finally, it’s your responsibility to be aware of the academic integrity policy and take the necessary steps to ensure that your use of AI-based tools is in compliance with this policy.
Religious Holidays#
According to the University Policy File, students should notify instructors of planned absences for religious observances by the end of the second week of classes. See the campus policy regarding religious observances for full details.
Land Acknowledgment#
For millennia, the Kumeyaay people have been a part of this land. This land has nourished, healed, protected and embraced them for many generations in a relationship of balance and harmony. As members of the San Diego State University community, we acknowledge this legacy. We promote this balance and harmony. We find inspiration from this land, the land of the Kumeyaay.